In recent years there has been rapid progress in the development of new biomedical engineering techniques, the applications of which provide patients with a better quality of life. Surgeries, metal prosthetics and medical devices, which help the injured to recover, have limitations, obstacles that biomedical engineering aims to overcome.
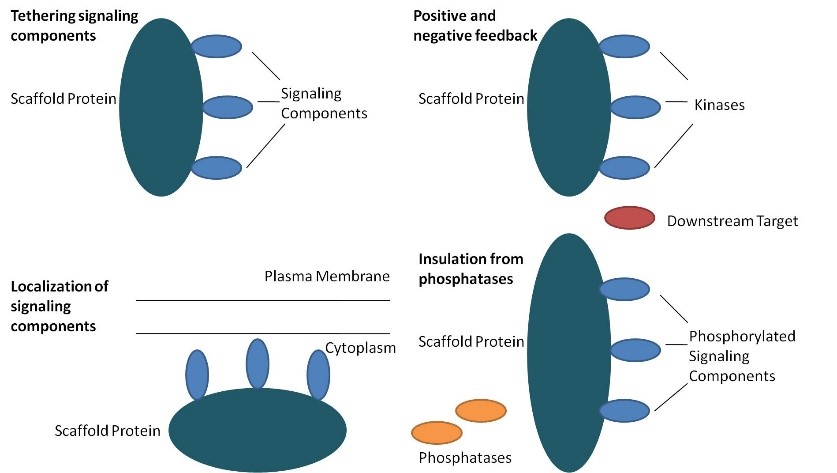
An important discovery made by scientists was the therapeutic effect of some plants in the regeneration and regeneration of bones and muscles. The medicinal action of plants was not unknown, as it is imprinted in the culture of many people. However, their role in bone mechanics has only recently begun to emerge. According to scientists, medicinal plants may have several of the answers to the limitations of multi-hour surgeries. Their study focused on herbs commonly used by South African traditional healers to treat bone fractures and relieve pain caused by osteoarthritis.
Fracture healing is a complex normal cell proliferative process, entailing the coordinated involvement of hematopoietic and immune cells within the bone marrow. In combination with vascular and skeletal precursor cells, mesenchymal stem cells are also recruited from the bloodstream and surrounding tissues. Many factors are involved, such as growth factors, inflammatory cytokines, antioxidant cells of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, hormones, amino acids and countless nutrients. Therefore, finding ways to heal and accelerate it requires innovative solutions.
The regenerative property of plants utilizes the existing structures of the organism and aims at the acceleration and activation of its biological responses, thus contributing to the regeneration of the bone and tissue that has been affected by the wound. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine are based on three basic principles: a) signals from tissues and organs of the body, b) stem cells that respond to the signals and c) scaffolds. Scaffolds are materials that work with biological systems to evaluate, heal, enhance, or replace any of the body's tissues or functions, such as mature bone, cartilage, skin cells, brain cells, and neurons. Thus, they repair or modify the function of cells in each cell phase - that is, how cells react during growth processes, such as gaining shape. In addition, they guide the growth of new tissues, indicating the proper path to follow and ensuring that cells receive the nutrients they need. But most of the biomaterial scaffolds used in clinical conditions do not bring all the expected results. That is why medicinal plants are a dynamic alternative.
To investigate their properties, Franca Nneka Alaribe and Keolebogile Shirley Motaung, a postdoctoral fellow and professor of tissue engineering, respectively, at Tshwane University of Technology in South Africa, conducted some experiments on the plants Eucomis ananalis and Pterocarpus angolensis (wild teak). 
The former has been shown to have a great beneficial effect on postoperative wound healing, while the latter promotes cartilage formation and regulates collagen, which is a substance rich in human bones and cartilage.
The researchers then combined the plants with scaffolds and pig fat cells. Laboratory tests showed that the cells were activated and the process for tissue bone formation was significantly enhanced by the use of this combination. The action of the scaffolds, in fact, improved when the scientists reacted with signals and stem cells as the combination of both plants with stem cells and enhancement of signaling gave better results than the classic scaffolds, being "hybrid scaffolds". They also contributed to the healing of wounds in vitro.

Several other scientists have studied new strategies based on the antioxidant, antimicrobial and regenerative effects of plants. Some plants, such as avocados, have the potential to promote "osteointegration" and bone growth by utilizing cytokines and other chemicals. Cytokines are a group of peptides used by immune cells to communicate with each other and with their environment. Studies show that they play a key role in controlling the immune response, inflammation, hematopoiesis, healing and regulating the normal function of cells in the body. These can enhance the expression of mediators useful in bone healing such as TGF-β1 and BMP-2 (picture).
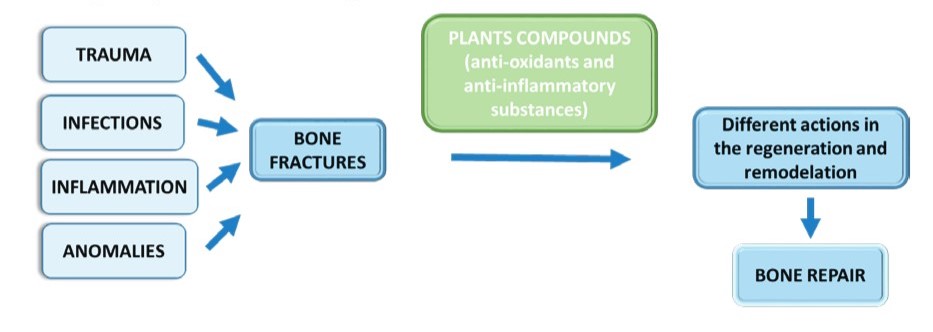
The findings of both surveys are encouraging, as they launch new ways of approaching recovery from difficult injury cases and significantly reduce medical costs.
Sources: https://theconversation.com/lab-studies-suggest-medicinal-plants-can-help-repair-human-bone-and-tissue-119011
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5512407/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2667099221000153
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334141459_The_Potential_Role_of_Medicinal_Plants_in_Bone_Regeneration